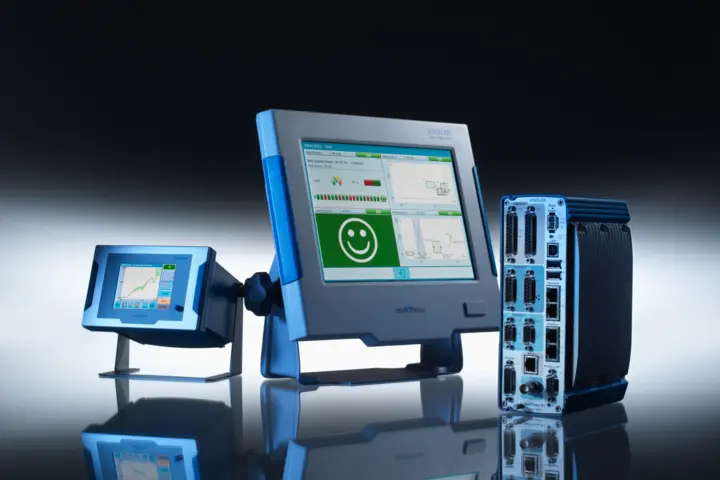
Winterthur, April 2018 – Global competition in the industrial manufacturing sector is increasing the requirements for quality and precision as time goes on. What is the most efficient and cost-effective way of optimizing and controlling the entire production chain? For many production enterprises, the solution has proven to be integrated monitoring of dynamic processes – more specifically, with the help of piezoelectric sensors.
The vision of Industry 4.0 is already becoming a successful reality today in numerous industrial applications – in sectors such as automobile manufacturing, medical technology and electrical engineering. Unprecedented optimization of all production processes is now possible thanks to the advance of digitization and the growth of machine and system networking. Consistent control of the production chain – with zero-defect production as the goal – is essential for any modern production business to hold its own in the market of the future.
Just a few years ago, virtually all products were still being inspected offline – i.e. after the manufacturing process as such. Nowadays, by contrast, more and more products are monitored during the manufacturing process – or 'inline' – as a way of avoiding unnecessary costs. For joining, assembly and testing processes, sensor technology based on the piezoelectric principle is a fundamental factor in optimizing production processes with zero-defect production as the goal. This technology is outstandingly suitable for measuring physical variables such as force, pressure, acceleration and torque.